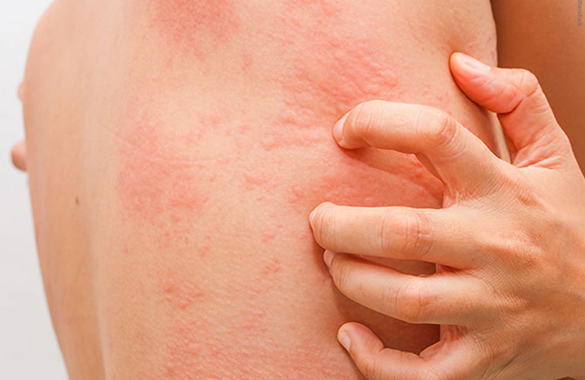
Hives or urticaria is a skin reaction that causes bumps, raised patches, or both to suddenly appear on the skin. These bumps and raised patches may appear swollen and are often itchy. The medical name for hives is urticaria.
Hives are not contagious and one cannot get hives by touching someone else’s hives or being around someone who has hives.
However, some people develop hives upon having a contagious disease like common cold. If someone with hives has a contagious disease, you can catch the contagious disease — but not hives.
Hives are often-itchy bumps and raised patches that develop when the body releases histamine.
Your body stores histamine inside certain cells. When your immune system recognizes a threat, it releases histamine and other chemicals. This cascade of chemicals can protect you from becoming seriously ill from an infection, spoiled fish, or a bug bite.
Sometimes, the immune system releases histamine when there is no real threat. This happens when people develop an allergic reaction.
When the body mistakenly releases histamine and hives develop, the cause is often one of the following:
If you have persistent hives, seeing a qualified dermatologist in Delhi can help you feel more comfortable. The dermatologist will examine your skin and will be able to tell you that if you have hives or it is some other ailment.
Here are some possible common triggers for an allergic reaction:
Hives are usually harmless and temporary. A single episode of hive tends to last for a few minutes to a few hours. Most hives clear within 24 hours.
As existing hives clear, new ones can form. New hives may appear on the same or different areas on the skin. Most people get new hives for a few days to a few weeks.
If new hives continue to appear for six weeks or longer, you have a condition called chronic hives.
When the cause of chronic hives is unknown, the condition is called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). People who have CSU get new hives daily — or almost daily. This can continue for months or years.
Development in batches –
Hives appear suddenly, causing a rash of smooth, raised swellings that tend to differ in size and shape. These swellings can be small, large, or somewhere in between. Some hives are as big as a hand.
Different colour from that of the skin –
If you have brown or black skin, hives are often the same colour as your skin, or slightly darker or lighter than your natural skin colour. People who have a light or medium complexion see red or pink hives.
Individual hives are temporary –
As some hives disappear, new hives may form. Most people have a case of hives for a few days to a few weeks. If new hives continue to appear for more than 6 weeks, you have a condition called chronic hives.
Skin itches, burns, or stings and warm sensation on touch –
Hives can itch, sometimes intensely. Some people say that hives burn or sting rather than itch. Because the skin is inflamed, hives often feel warm to the touch.
Raised spots or patches –
Sometimes, hives run together, as shown here. The large, raised patches are called plaques.
https://dermasureclinic.com/wp-admin/admin.php?page=newsletters-lite-upgrade
Living with urticaria can affect one’s quality of life. Some people claim to feel a loss of control because they never know when hives will appear. Though, hives often worsen during the night. This can make it difficult to sleep.
A continual loss of sleep can make you feel tired and irritable. Some people develop anxiety or depression. All of this can affect the person’s ability to do well in school or at work.
In chronic cases, urticaria or hives must be addressed and treated by a certified dermatologist. Luckily at DermaSure, we have quality expertise to treat your urticaria through careful diagnosis and safe treatments.
After the cause for urticaria or hives is known, we draft your treatment plan that is tailored to your needs and may include one or more of the following:
Prax lotion or menthol cream is advised for temporary relief from the itch.
When hives are severe, a medication like prednisone can reduce the inflammation and itch. For milder hives, your dermatologist may prescribe a corticosteroid that you apply to your skin to help relieve the itch.
This is an injectable medication that is used to treat chronic hives. It’s prescribed when antihistamines fail to work.
This medication can help control the itch and swelling. You can buy some antihistamines like cetirizine, loratadine, and Benadryl without a prescription. Benadryl can make you sleepy, so it’s best taken at bedtime. If you need a stronger antihistamine, your dermatologist may prescribe doxepin.
(also called phototherapy) This is a non-invasive treatment that can be effective when antihistamines don’t work. It requires several trips a week for a few months to your dermatologist or phototherapy treatment centre.
With these latest treatment options and rehabilitation options, you can trust DermaSure to get relief from Hives and make the most of your life! Visit our clinic to get a personalised plan for Urticaria treatment.
Yes, stress can be a common trigger for urticaria. Emotional stress and anxiety can lead to the release of certain chemicals in the body that can cause hives to appear or worsen existing symptoms.
No, urticaria itself is not contagious. It is not caused by an infection or a contagious agent. However, certain underlying causes of urticaria, such as a viral infection, may be contagious.
Yes, certain medications can trigger urticaria in some individuals. Common culprits include antibiotics (such as penicillin), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and aspirin. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about any medication allergies or previous reactions.
In some cases, urticaria symptoms can involve an underlying medical condition, such as an autoimmune disorder, thyroid disease, or a chronic infection. If hives persist or recur frequently, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Urticaria treatment involves identifying and avoiding triggers, practising good skincare, and taking appropriate medications as prescribed. Applying cool compresses to the affected area, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and using fragrance-free products can help alleviate symptoms. It may also be helpful to keep a diary to track potential triggers and discuss them with your healthcare provider for personalised management strategies.
Submit your review | |
Leave Them To #1 Skin & Hair Specialist In Delhi