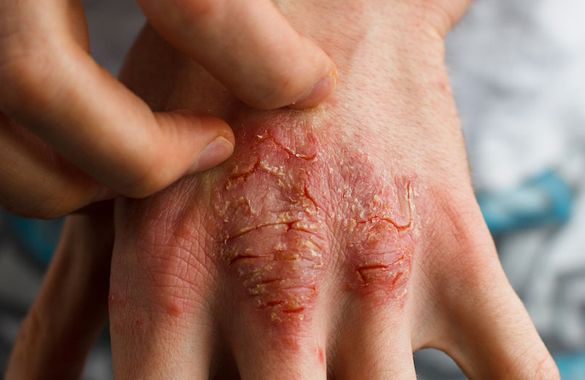
Eczema is characterised by inflamed, irritated, and frequently itchy skin. Multiple conditions can present with eczematous rashes including atopic dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or contact dermatitis.
You get this skin condition when anything touching your skin either irritates it or sets off an allergic reaction. Skin itching is frequently the initial symptom, followed by a rash. Here are some common reasons that are conducive to eczema:
Eczema can affect people of all ages, but it commonly begins in infancy or early childhood. It is estimated that up to 20% of children and 3% of adults worldwide are affected by eczema.
Those with a family history of allergies or asthma are more prone to developing eczema. Additionally, factors such as environmental triggers, dry skin, immune system dysfunction, and genetic predisposition contribute to the development of eczema.
Eczema symptoms can appear anywhere on the body and vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms that can appear in any kind of eczema include:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) can present with any of the lesions described above. However, the rash follows a characteristic distribution that varies with age.
Infantile AD
In babies, the rash can appear as dry, scaly or red, oozing patches especially over the cheeks and scalp.
Childhood AD
It is characterised by itchy, scaly patches in the creases of the elbows and knees. It can also appear on the neck, wrists, ankles and legs.
In some cases, thickening of skin may become noticeable due to chronic scratching
Adult AD
When AD develops after 18 years of age, it presents as extremely dry, itchy skin that gets irritated easily. It can also present as hand eczema or eyelid eczema.
Different types of eczema show varied symptoms, and the treatment differs. However, being mindful of certain precautions can help mitigate the symptoms or flare-ups.
Eczema can get the best of a patient, especially if they’re grappling with symptoms like burning sensation, redness, and excessive itching. These can cause problems in lifestyle, difficulty staying at ease in the work environment, hamper sleep and so on.
At DermaSure, we handle eczema cases with proper care. First, we focus on knowing the causes of eczema and possible triggers and then move to treatment options suited for the case:
An anti-inflammatory medicine, like CaN inhibitors, that works by reducing immunological response and so reducing inflammation is recommended.
These medications aid in reducing scratching, which can aggravate eczema by bleeding. It soothes the patient while impeding future development.
These may be administered for infections depending on the situation.
Oral medications (injections or tablets) that lower inflammation and improve immune system performance.
Steroid sparing agents may be used in cases where eczema worsens after stopping corticosteroids and long term treatment is required.
Ciggers, using proper skincare routines, and following a treatment plan, individuals with eczema can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.urrently, there is no known cure for eczema. However, it can be effectively managed and controlled with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes. By identifying triggers, using proper skincare routines, and following a treatment plan, individuals with eczema can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
To manage and control eczema flare-ups, it is important to establish a comprehensive treatment plan in consultation with a healthcare professional. This may involve using moisturisers to keep the skin hydrated, avoiding triggers such as certain fabrics or irritants, taking prescribed medications or topical corticosteroids, and practising good skincare habits, including gentle cleansing and regular moisturization.
There is a genetic component to eczema, and individuals with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma may be more prone to developing the condition. However, eczema can also occur in individuals with no family history of the condition.
While food allergies or sensitivities can trigger eczema flare-ups in some individuals, it is not a common cause for everyone. Common food triggers include dairy products, eggs, nuts, soy, wheat, and seafood. Identifying and avoiding specific allergens may help reduce symptoms, but it is important to consult an allergist or healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Eczema cannot be spread. Eczema is the same way. It is impossible to contract someone else’s scaly, itchy, or dry skin simply by being near or even touching them. It is never contagious to have eczema.
Flares of eczema can persist for two weeks or longer, contingent upon the aetiology. Remission can be reached faster if the reason for the flare is found and treated right away. Although eczema cannot be cured, its symptoms can be controlled.
Submit your review | |
Leave Them To #1 Skin & Hair Specialist In Delhi